In
order to transfer a “hex code” to the microcontroller, it is necessary to
provide a cable for serial communication and a special device, called
programmer, with software. There are several ways to doit.
A
large number of programs and electronic circuits having this purpose can be
found on the Internet. Do as follows: open hex code document, set a few
parameters and click the icon for compiling. After a while, a sequence of zeros
and ones will be programmed into the microcontroller through the serial connection
cable and programmer hardware. What's left is to place the programmed chip into
the taget device. In the event that it is necessary to make some changes in the
program, the previous procedure may be repeated an unlimited number of times.

The
end or...?
This
section briefly describes the use of MPLAB and programmer software developed by
Mikroelektronika. Everything is very simple...
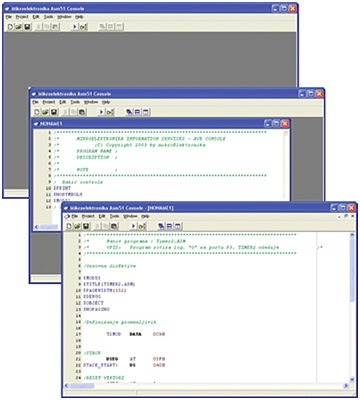
Start the program
Mikroelektronika Asm51 Console. The window appears...
...Open a new document: File
-> New. Write your program or copy text...
... Save and name your document:
File -> Save As... (Document name is limited to 8 characters!)
Finally, to compile program into
HEX code select: Project -> Build or click the 'play' icon.
If everything works properly, the
computer will respond with a short report.

The
program is written and successfully compiled. All that's left is to dump the
program to the microcontroller. For this purpose it is necessary to have a
software that takes the written and compiled program and passes it to the
microcontroller.
Start
the program 8051 Flash_setup.exe...

Program
installation is performed as usually - just click Next, Accept, Next...
...and
finally - Finish!
The
program has been installed and ready for use. The settings are easily performed
so that there is no need for additional explanations (the type of the
microcontroller, frequency and clock oscillator etc.).
• Connect
the PC and programmer via a USB cable;
• Load
the HEX code using command: File -> Load HEX; and
• Click
the 'Write' push button and wait...

That’s
all! The microcontroller is programmed and everything is ready for operation.
If you are not satisfied, make some changes in the program and repeat the
procedure. Until when? Until you feel satisfied...
Development systems

A
device which in the testing program phase can simulate any environment is
called a development system. Apart from the programmer, the power supply unit
and the microcontroller’s socket, the development system contains elements for
input pin activation and output pin monitoring. The simplest version has every
pin connected to one push button and one LED as well. A high quality version
has LED displays, LCD displays, temperature sensors and all other elements
which can be supplied with the target device. These peripherals can be
connected to the MCU via miniature jumpers. In this way, the whole program may
be tested in practice during its development stage, because the microcontroller
doesn't know or care whether its input is activated by a push button or a
sensor built in a real device.

7.2 Easy8051A Development System
The
Easy8051A development system is a high-quality development system used for
programming 8051 compatible microcontrollers manufactured by Atmel. In addition
to chip programming, this system enables all the parts of the program to be
tested as it contains most components which are normally built in real devices.
The
Easy8051A development system consists of:
• Sockets
for placing microcontrollers in (14, 16, 20 and 40- pin packages)
• Connector
for external power supply (DC 12V)
• USB
programmer
• Power
Supply Selector (external or via USB cable)
• 8
Mhz Quartz Crystal Oscillator
• 32
LEDs for output pin state indication
• 32
push buttons for input pin activation
• Four
7-segment LED displays in multiplex mode
• Graphic
LCD display
• Alphanumeric
LCD display (4- or 8- bit mode)
• Connector
and driver for serial communication RS232
• Digital
thermometer DS1820
• 12-
bit A/D converter (MCP3204)
• 12-
bit D/A converter (MCP4921)
• Reference
voltage source 4.096V (MCP1541)
• Multiple-pin
connectors for direct access to I/O ports
The
following text describes in short some circuits within this development system.
It is rather illustration of its features than complete manual. Besides, by
learning about this device, one understands that microcontrollers and its tools
are intended to everybody, not only to the privileged.
Sockets


All
microcontrollers manufactured by Atmel appear in a few standard DIP packages.
In order to enable their programming using one device, corresponding pins
(having the same name) on sockets are connected in parallel. As a result, by
being placed in the appropriate socket, each microcontroller is automatically
properly connected. Figure on the right shows a microcontroller in 40-pin
package and connection of one of its I/O pins (P1.5). As seen, the pin can be
connected to an external device (connector PORT1), LED (microswitch SW2), push
button or resistor through connectors. In the last two cases, polarity of
voltage is selected using on-board jumpers.

Programmer

The
purpose of the programmer is to transfer HEX code from PC to appropriate pins
and provide regular voltage levels during chip programming as well. For this
development system, the programmer is built in it and should be connected to PC
via USB cable. When the process of programming is completed, pins used for it
are automatically available for other application.

Development system power supply

There
is a connector on the development board enabling commection to external power
supply source (AC/DC, 8-16V). Besides, voltage necessary for device operation
can also be obtained from PC via USB cable. Jumper J5 is used for power supply
selection.

8MHz
Oscillator

The
EASY8051A development system has built-in oscillator used as a clock signal
generator. The frequency of this oscillator is stabilized by 8Hz quartz
crystal. Besides, it is also possible to select internal RC oscillator during
chip programming,.

LEDs for
output pin state indication

Each
I/O port pin is connected to one LED which enables visual indication of its
logic state. In the event that the presence of directly polarized LEDs and
serial resistors is not acceptable in some applications, DIP switch SW2 enables
them to be disconnected from the port.

Push
buttons for input pin activation

Similar
to LEDs, each I/O port pin is connected to one push button on the development
board. It enables simple activation of input pins. Jumper J6 is used for selecting
voltage polarity (+ or -) brought to pins by pressing appropriate push button.

7-segment
LED displays

Being
often applied in the industry, four high-performance LED displays set in
multiplex mode belong to the development system. Display segments are connected
to the port P0 via resistors. Transistor drivers used for activating individual
digits are connected to the first four port P1 pins. It enables programs using
7-segment displays to be tested with minimum use of I/O ports. Similar to LEDs,
DIP switch SW2 enables transistor drivers to be disconnected from
microcontroller pins.

LCD
displays
The
EASY8051A development system provides connection to eather graphic or
alphanumeric LCD display. Both types of displays are connected by being placed
into appropriate connector and by switching position of the jumper J8. If
displays are not in use, all pins used for their operation are available for
other applications. Apart from connectors, there is also a potentiometer for
contrast regulation on the board.

Serial
communication via RS232

In
order to enable programs using serial communication to be tested, the
development system has built in standard 9-pin SUB-D connector. The MAX232 is
used as a voltage regulator.
Similar
to other built-in circuits, electronics supporting serial communication can be
enabled or disabled by using jumpers J9 and J10.

DS1820
Digital thermometer

Temperature
measurement is one of the most common tasks of devices which operate in the
industry. For this reason, there is a circuit DS1820 on the EASY8051A
development system which measures temperature in the range of -55 to +125oC
with accuracy greater than 0.50. Results of measurement are transferred via
serial communication to the pins P3.3 or P2.7. Jumper J7 is used for selecting
pins for data reception. In the event that no jumper is installed, port pins
are available for other applications.

12-bit
A/D converter MCP3204

A
built-in 12-bit AD Converter MCP3204 has four input channels connected to
on-board connectors. Data are interchanged with the microcontroller via SPI
serial communication system using pins P1.5, P1.6, P1.7 and P3.5. If A/D
converter is not in use, these pins can be used for other applications (DIP
switch SW1). In order to check operation, there is a potentiometer on the
development board used as a variable voltage source. It can be brought to the
converter’s input pins using one of four jumpers J12. As a special convenience,
a reference voltage source MCP1541 (4,096V) is built in. Jumper J11 is used to
select whether converter will use this voltage or 5V.

12-bit
D/A converter MCP4921

Digital
to analog conversion (D/A) is another operation ofen performed by the
microcontroller in practice. For this reason, there is a special on-board chip
which interchanges data with the microcontroller via SPI communication system.
It can also generate analog voltage in 12-bit resolution on its output pin.
When it is not in use, all microcontroller pins are available for other
applications using DIP switch SW1. Similar to A/D converter, jumper J11 is used
for selecting reference voltage.

Connectors
for direct access to I/O ports

In
order to enable microcontroller ports to be directly connected to additional
components, each of them is connected to one on-board connector. Besides, two
pins of each connector are connected to power supply voltage while each pin can
be connected to + or - polarity of voltage via resistors (pull up or pull down
resistors). Presence and connection of these resistors are determined by
jumpers. Jumper J3 which controls port P3 is shown in figure on the right.



No comments:
Post a Comment